Latest Updates
- President Trump signed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act into law on July 4, 2025.
- This update adds refined modeling results reflecting the amendments made in the Senate to the final version of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act, now passed by both chambers of Congress to be signed by the president.
- The One Big Beautiful Bill Act was amended before being passed out of the Senate.
Key Findings
-
- Extending the expiring 2017 TaxA tax is a mandatory payment or charge collected by local, state, and national governments from individuals or businesses to cover the costs of general government services, goods, and activities. Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) would decrease federal tax revenue by $4.5 trillion from 2025 through 2034. Long-run GDP would be 1.1 percent higher, offsetting $710 billion, or 16 percent, of the revenue losses. Long-run GNP (a measure of American incomes) would only rise by 0.4 percent, as some of the benefits of the tax cuts and larger economy go to foreigners in the form of higher interest payments on the debt.
- President Trump has called for permanent extension of the 2017 tax cuts, additional policies— including no taxes on tips, overtime pay, and Social Security benefits for retirees—as well as creation of a deduction for auto loan interest for American made cars. He has also promised higher taxes on US imports through a series of new tariffs.
- Lawmakers will use the budget reconciliation process to enact new tax cuts. Reconciliation is a fast-track option that overcomes the Senate filibuster and can be used to enact tax, spending, and debt limit changes outlined in a budget resolution with specified targets or limits for deficit changes within the budget window.
- Separately from the reconciliation process in Congress, President Trump is imposing tariffs that will raise revenue and reduce economic output.
- Lawmakers have passed legislation called the “One Big Beautiful Bill Act” to make the expiring tax cuts permanent, provide additional tax cuts and changes to the tax code, and reduce spending.
- President Trump signed the bill into law on July 4, 2025.
The Latest
- On July 4, 2025: President Trump signed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act into law.
- On July 3, 2025: We estimate the Senate-passed version of the “One Big Beautiful Bill” as agreed to by the House would increase long-run GDP by 1.2 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $5.0 trillion from 2025-2034 on a conventional basis. Dynamic feedback will reduce the revenue loss of by bill by about 19 percent to $4.1 trillion, while spending reductions of nearly $1.1 trillion will reduce the dynamic deficit increase to $3 trillion from 2025-2034.
- July 1, 2025: The One Big Beautiful Bill Act bill was amended before being passed out of the Senate.
- June 30, 2025: We estimate that the Senate Finance Committee’s version of the “One Big Beautiful Bill” would increase long-run GDP by 1.2 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $5 trillion between 2025 and 2034, on a conventional basis. Combined with the nearly $1.2 trillion in spending reductions estimated by the Congressional Budget Office (CBO), we estimate the Senate version of the OBBB would increase federal budget deficits by nearly $2.9 trillion from 2025 through 2034 on a dynamic basis.
- June 24, 2025: We estimate that the Senate Finance Committee’s version of the “One Big Beautiful Bill” would increase long-run GDP by 1.1 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $4.7 trillion from 2025-2034 on a conventional basis after incorporating JCT estimates for items not scored by Tax Foundation, updating our modeling of the SALT pass-through workarounds, and adding proposed changes to the premium tax creditA tax credit is a provision that reduces a taxpayer’s final tax bill, dollar-for-dollar. A tax credit differs from deductions and exemptions, which reduce taxable income rather than the taxpayer’s tax bill directly. , earned income tax credit and child tax credit into our distributional estimates.
- June 18, 2025: We estimate on a preliminary basis that the Senate Finance Committee’s version of the “One Big Beautiful Bill” would increase long-run GDP by 1.1 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $4.8 trillion from 2025-2034 on a conventional basis.
- June 13, 2025: We updated our description of the bill’s changes to spending and revenue to better illustrate the share of revenue losses that are offset by dynamic revenue.
- June 6, 2025: We updated our analysis of the version of the “One Big Beautiful” bill that passed the House of Representatives. Our estimate of federal tax revenue losses fell back to $4.0 trillion from 2025 through 2034. Our estimate of the long-run GDP effect stayed at 0.8 percent.
- May 22, 2025: The “One Big Beautiful” bill was amended before being passed out of the House of Representatives. Tax policy changes include a more generous SALT deduction cap, changes to inflation indexingInflation indexing refers to automatic cost-of-living adjustments built into tax provisions to keep pace with inflation. Absent these adjustments, income taxes are subject to “bracket creep” and stealth increases on taxpayers, while excise taxes are vulnerable to erosion as taxes expressed in marginal dollars, rather than rates, slowly lose value. for the alternative minimum tax, accelerated phaseouts and adjustments for IRA green energy credits, a slight increase in the proposed international tax rates, and an expanded limit on itemized deductions, among other smaller changes. The long-run GDP effect increased slightly to 0.8 percent and federal tax revenue losses increased slightly to $4.1 trillion from 2025 through 2034 on a conventional basis.
- May 13, 2025: We estimate the House GOP’s “One Big Beautiful” tax bill under markup would increase long-run GDP by 0.6 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $4.0 trillion from 2025 through 2034 on a conventional basis.
- May 5, 2025: We estimate the tariffs imposed as of May 2025 would raise $2.1 trillion of revenue from 2025 through 2034, while reducing US economic output by 0.8 percent in the long run.
- April 10, 2025, the House adopted the Senate’s amended version of the budget resolution, which allows $5.3 trillion in deficit-financed tax cuts (the combination of $3.8 trillion of tax cuts assumed to be “costless” under a current policy baseline plus $1.5 trillion in additional deficits permitted), deficit increases of $521 billion on defense and immigration spending, a minimum of $4 billion in spending cuts, and an increase in the debt limit of up to $5 trillion.
- April 2, 2025, the Senate introduced an updated budget resolution to provide new guidance to its committees on tax and spending policy changes. It adopts the instructions in the House resolution for the House committees while instructing the Senate Finance Committee to make tax policy changes that reduce revenue by up to $1.5 trillion over 10 years against a current policy baseline, which assumes an additional $3.8 trillion in tax cuts. While the $3.8 trillion would not officially score as a deficit increase against a current policy baseline, it effectively permits $5.3 trillion in deficit-financed tax cuts.
- The Senate resolution gives the Chair of the Senate Budget Committee the ability to revise the numbers using a current tax policy baseline and instructs the Senate Finance Committee to propose an increase in the debt limit by up to $5 trillion.
- The Senate resolution gives the Chair of the Senate Budget Committee the ability to revise the numbers using a current tax policy baseline and instructs the Senate Finance Committee to propose an increase in the debt limit by up to $5 trillion.
- February 25, 2025, the House passed a budget resolution to start the reconciliation process, specifying reductions in taxes and spending over the next decade relative to a current law baseline. The House budget resolution allows a $4.5 trillion increase in the deficit from tax cuts over the next decade so long as spending is cut by $1.7 trillion. If spending is not cut by $1.7 trillion, the cap on tax cuts will be reduced dollar-for-dollar; if spending is cut by more than $1.7 trillion, the cap on tax cuts will be increased by the same.
- February 21, 2025, the Senate approved its own budget resolution to start the reconciliation process, but it does not permit any tax cuts.
Compare Tax Plans
Details
- On July 4, 2025: President Trump signed the One Big Beautiful Bill Act into law.
- On July 3, 2025: The House passed the Senate's One Big Beautiful Bill Act.
- On July 1, 2025, the One Big Beautiful Bill Act was amended before being passed out of the Senate.
- On June 27, 2025, the Senate released a new version of the legislative text for the One Big Beautiful Bill (OBBB).
- On June 16, 2025, the Senate Finance Committee released text for the tax components of the Senate version of the “One Big Beautiful Bill,” which notably includes permanence for major individual and corporate provisions of the TCJA. The Senate amended the bill before final passage on July 1, 2025.
Analysis
- Our analysis finds the major tax provisions included in the Senate "One Big Beautiful Bill Act" Tax Plan would increase long-run GDP by 1.2 percent, hours worked by 938,000 jobs, wages by 0.4 percent, and the capital stock by 0.7 percent.
- We estimate the tax provisions would reduce federal tax revenue by $5 trillion between 2025 and 2034, on a conventional basis. On a dynamic basis, incorporating the projected increase in long-run GDP of 1.2 percent, the dynamic score of the tax provisions falls to $4.1 trillion, meaning economic growth pays for 19 percent of the tax cuts.
- By making key provisions like 100 percent bonus depreciationBonus depreciation allows firms to deduct a larger portion of certain “short-lived” investments in new or improved technology, equipment, or buildings in the first year. Allowing businesses to write off more investments partially alleviates a bias in the tax code and incentivizes companies to invest more, which, in the long run, raises worker productivity, boosts wages, and creates more jobs. and expensing for R&D permanent, the Senate Finance tax bill is a more pro-growth bill that would improve stability, taxpayer certainty, and investment incentives.
- Combined with nearly $1.1 trillion in spending reductions, we estimate the Senate bill would increase budget deficits by $3 trillion from 2025-2034 before added interest costs. Interest costs would add $725 billion to the 10-year deficit impact, bringing the total deficit increase on a dynamic basis to nearly $3.8 trillion inclusive of additional interest payments due to increased borrowing.
- The increased borrowing under the bill would reduce American incomes (GNP) by 0.6 percent, creating a wedge between the increase in long-run GDP of 1.2 percent and the increase in long-run GNP of 0.9 percent.
Senate "One Big Beautiful Bill Act" Tax Plan: Topline Analysis
| 10-Year Conventional Revenue Estimate (Billions) | 10-Year Dynamic Revenue Estimate (Billons) | 10-Year Dynamic Deficit Increase Including Spending Cuts (Billions) | Long-Run GDP | Long-Run GNP | Long-Run Pre-Tax Wages | Long-Run Hours Worked Converted to FTE Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -$5,041.3 | -$4,104.4 | $3,036.1 | +1.2% | +0.9 | +0.4% | +938,000 |
See Full Analysis
Related Resources:
-
- “Big Beautiful Bill” Senate Tax Plan: Details and Analysis See more
- The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly in the One Big Beautiful Bill See more
- The One Big Beautiful Tax Bill: What’s In It, What’s Out See more
- How Would the Proposed Additional Senior Deduction Compare to No Tax on Social Security? See more
- Will the Big Beautiful Bill Lead to an Economic Boom or Just Modestly Higher Growth? See more
- The Senate Finance Committee’s New International Tax Package: A First Look See more
- A Partial Defense of the QBAI Exclusion See more
- Senate Softens Blow for Pass-Throughs Using Current SALT Workarounds See more
Details
- On May 22, the House Rules Committee amended elements of the House Ways and Means legislative text related to SALT, IRA green energy credits, international taxes, the alternative minimum tax, and itemization deductions. The broader bill was passed out of the House of Representatives.
- On May 12, the House Ways and Means CommitteeThe Committee on Ways and Means, more commonly referred to as the House Ways and Means Committee, is the chief tax-writing committee in the US. The House Ways and Means Committee has jurisdiction over all bills relating to taxes and other revenue generation, as well as spending programs like Social Security, Medicare, and unemployment insurance, among others. released pre-mark legislative text to extend the expiring 2017 tax cuts and provide additional changes to the US tax system ahead of a markup hearing on May 13.
- The legislative text introduced by the Ways and Means Committee cuts taxes by less than the budget resolution instructions, implying either that spending reductions have fallen short of the target or that lawmakers are leaving room for further negotiations over certain tax items.
Analysis
- On July 3, the House agreed to the Senate amendment of the bill. The analysis below reflects the original House-passed version of the bill.
- Our preliminary analysis finds the tax provisions included in the House reconciliation bill would increase long-run GDP by 0.8 percent, increase hours worked by 983,000 jobs, increase American incomes as measured by GNP by 0.7 percent, increase wages by less than 0.05 percent, and increase the capital stock by 0.2 percent.
- We estimate the tax provisions would reduce federal tax revenue by $4.0 trillion between 2025 and 2034, on a conventional bases. On a dynamic basis, incorporating the projected increase in long-run GDP of 0.8 percent, the dynamic score of the tax provisions falls to $3.1 trillion, meaning economic growth pays for 22 percent of the tax cuts. The bill’s net spending cuts of about $1.5 trillion lead to a combined budget deficit increase of $1.7 trillion over the 10-year budget window on a dynamic basis.
- Overall, the bill would prevent tax increases on 62 percent of taxpayers that would occur if the TCJA expired as scheduled. However, by introducing narrowly targeted new provisions and sunsetting the most pro-growth provisions, like bonus depreciation and research and development (R&D) expensing, it leaves economic growth on the table and complicates the structure of the tax code.
House Big, Beautiful Bill Act Tax Plan: Topline Preliminary Estimates
| 10-Year Conventional Revenue Estimate (Billions) | 10-Year Dynamic Revenue Estimate (Billons) | 10-Year Dynamic Deficit Increase Including Spending Cuts (Billions) | Long-Run GDP | Long-Run GNP | Long-Run Wages | Long-Run Hours Worked Converted to FTE Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -$4,006.5 | -$3,111.5 | -$1,724.6 | +0.8% | +0.7% | Less than +0.05% | 983,000 |
Related Resources:
- A More Generous SALT Deduction Cap in the Big, Beautiful Bill Would Cost Revenue and Primarily Benefit High Earners See more
- House Tax Package Could Double Economic Growth Impact by Prioritizing Permanence for TCJA Business Provisions See more
- Breaking Down the Senior Deduction in the One, Big, Beautiful Bill See more
- ‘Trump Accounts’ Could Be Better. Here’s How. See more
- How the IRA Provisions (and Scores) Have Changed See more
- How Does the House-Passed Tax Bill Change the Section 199A Pass-Through Deduction? See more
- The Remittances Tax: High Paperwork, Low Payoff See more
- How Would the Proposed $4,000 Senior Deduction Compare to No Tax on Social Security? See more
- House “One Big Beautiful Bill” Riddled with Temporary Tax Policy See more
- House GOP’s Approach to the IRA Clean Energy Tax Credits: Five Things to Know See more
- Current Trump Tariffs Threaten to Offset Benefits of Promised Tax Cuts See more
- The One Big Beautiful Bill, Explained Listen now
- State Implications of the One, Big, Beautiful Bill See more
- SALT Cap Workarounds for Some Pass-Through Entities Are Threatened by One, Big, Beautiful Bill See more
- What Are the Goals of Retaliatory Tax Policies? See more
- Three Corporate Tax Hikes That Would Undermine TCJA’s Improvements to Competitiveness See more
- Raising the Top Income Tax Rate Would Offset Economic Benefits of TCJA Individual Permanence See more
- Growth Should Be a Key Consideration if Corporate SALT Is Limited See more
Details
- On the campaign trail, and reiterated in his March 4 joint address to Congress, President Trump called for permanence for the 2017 tax law, restoring the state and local tax (SALT) deduction, reducing the corporate tax rate for domestic production, exempting various types of income from the income tax, repealing green energy tax credits, and imposing steep new tariffs.
Analysis
- Some of Trump’s tax proposals are well-designed and would be efficient ways to promote long-run economic growth, such as permanent expensing for machinery, equipment, and research and development (R&D).
- Some of his tax proposals are poorly designed and would worsen the structure of the tax code while only creating a muted impact on long-run economic growth, such as the exemptions for tips and Social Security income.
- Worse yet, Trump’s reliance on import tariffs to offset the cost of tax cuts come with major downsides. Tariffs are a particularly distortive way to raise revenue, especially as they invite foreign retaliation. We estimate Trump’s proposed tariffs and partial retaliation from all trading partners would together offset more than two-thirds of the long-run economic benefit of his proposed tax cuts.
- During the campaign, we estimated Trump’s tax proposals would increase long-run GDP by 0.8 percent, the capital stock by 1.7 percent, wages by 0.8 percent, and employment by 597,000 full-time equivalent jobs. We also estimated the proposals would increase the 10-year budget deficit by $3 trillion conventionally and $2.5 trillion dynamically.
Trump 2024 Campaign Tax Plan: Topline Preliminary Estimates
| 10-Year Conventional Revenue (Billions) | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Gross National Product (GNP) | Long-Run Pretax Wages | Long-Run Hours Worked Converted to FTE Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -$3,013.2 | +0.8% | -0.1% | +0.8% | +597,000 |
Details
- President Trump has imposed new tariffs on nearly all US trading partners as well as on specific products, affecting more than 70 percent of US imports. While the tariffs are not formally or officially part of the reconciliation context, they will have economic and revenue effects to consider alongside the tax package Congress produces.
Analysis
- The tariffs imposed and scheduled to take effect as of April 2025 would increase federal tax revenue by $2.1 trillion from 2025 through 2034 on a conventional basis and decrease after-tax incomes by 1.2 percent on average.
- Before accounting for foreign retaliation, Tax Foundation estimates the tariffs will reduce long-run US output by 0.7 percent.
Trumps Tariffs: Topline Preliminary Estimates
| 10-Year Conventional Revenue (Billions) | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Long-Run Pretax Wages | Long-Run Hours Worked Converted to FTE Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|
| $2,080.4 | -0.7% | 0.0% | -685,000 |
Details
- Beginning January 1, 2026, most provisions of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) will expire. Additionally, several business provisions have already expired or are phasing out. Without Congressional action, expiration of the individual provisions would increase taxes for 62 percent of taxpayers, while extension will significantly reduce federal revenues over the coming decade.
Analysis
- Over the 2025 through 2034 budget window, permanence for the expiring TCJA individual provisions will reduce federal tax revenue by $3.6 trillion ($3.2 trillion dynamically), the expiring estate tax provisions by $240 billion ($240 billion dynamically), and the expiring business provisions by $648 billion ($351 billion dynamically).
- Long-run GDP would be 1.1 percent higher, offsetting $710 billion, or 16 percent, of the revenue losses.
- The $4.5 trillion reduction in tax revenues would increase the budget deficit and push up interest costs by an estimated $941 billion ($806 billion dynamically). Long-run GNP would only rise by 0.4 percent, as some of the benefits of the tax cuts and larger economy go to foreigners in the form of higher interest payments on the debt.
- As a result of the tax cuts, after-tax incomes would rise by 2.9 percent (3.4 percent dynamically) in 2026 on average. The share of filers who itemize would drop from 33 percent to 13 percent, and 62 percent of filers would see a tax cut from extending the individual provisions.
TCJA Permanence: Topline Preliminary Estimates
| 10-Year Conventional Revenue (Billions) | Gross Domestic Product (GDP) | Gross National Product (GNP) | Long-Run Pretax Wages | Long-Run Hours Worked Converted to FTE Jobs |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| -$4,506.3 | +1.1% | +0.4% | +0.5% | +847,000 |
See Full Analysis
What is Budget Reconciliation?
In 2017, Republicans used a procedure called budget reconciliation to pass the TCJA. Democrats used it for the American Rescue Plan Act (ARPA) in 2021, and the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in 2022. Reconciliation is a fast-track option to enact tax, spending, and debt limit changes outlined in a budget resolution, notably bypassing a filibuster in the Senate that would otherwise require 60 votes to avoid. Budget reconciliation allows Republicans to rely on a party-line vote for legislation, but they still face slim majorities in both chambers.
Lawmakers can specify targets or limits on reductions or increases in the deficit within the budget window. The “Byrd rule” limits what can be included in a reconciliation bill, disallowing policy changes that don’t affect spending or revenue, and disallowing changes that increase the deficit outside of the budget window. Reconciliation also specifically prohibits changes to Social Security.
What is the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act?
The 2017 Trump Tax Cuts, known as the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA), reduced average tax burdens for taxpayers across the income spectrum and temporarily simplified the tax filing process through structural reforms. It also boosted capital investment by reforming the corporate tax system and significantly improved the international tax system.
At the end of 2025, the individual portions of the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act expire all at once. Without congressional action, 62 percent of filers could soon face a tax increase relative to current policy in 2026. At the same time, the price tag for extending the 2017 Trump tax cuts is in the trillions.
tax Calculator Interactive map TCJA Archives
The Path Forward: Principled, Pro-Growth, Fiscally Responsible Tax Reform
Congress is staring down the expiration of the TCJA, and the Tax Foundation is prepared to provide insight and analysis on the policies at stake. Since its enactment in 2017, the Tax Foundation team has studied the TCJA’s underlying construction and resulting strengths and weaknesses. We have also analyzed fundamental reforms that would dramatically improve the US tax system to support economic growth as well as greater efficiency and simplicity.
Whether lawmakers target fundamental tax reform or follow the outline of the TCJA, they will confront decisions on what to prioritize in this forthcoming round of tax reform. In that regard, staying within the overall TCJA construct, the Tax Foundation team has analyzed difficult, but revenue-neutral ways to build a pro-growth set of reform options that would not significantly worsen the deficit once changes to the economy are considered or substantially change the distribution of the tax burden across the income scale.
Related Resources

The Good, the Bad, and the Ugly in the One Big Beautiful Bill Act
The One Big Beautiful Bill Act makes many of the individual tax cuts and reforms of the TCJA permanent. It improves upon the TCJA by making expensing for R&D and equipment permanent. However, for the most part, it does not include further structural reforms, and instead introduces many new, narrow tax breaks to the code, adding complexity and raising revenue costs.
7 min read
“One Big Beautiful Bill Act” Tax Policies: Details and Analysis
We estimate the One Big Beautiful Bill Act would increase long-run GDP by 1.2 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $5 trillion over the next decade on a conventional basis.
11 min read
The One Big Beautiful Tax Bill: What’s In It, What’s Out
Congress is racing to pass the One Big Beautiful Tax Bill before the July 4 deadline. In this episode, Kyle Hulehan and Erica York break down what just happened over the weekend, what’s actually in the bill, and what comes next as the House and Senate try to reconcile their differences.

The Senate Finance Committee’s New International Tax Package: A First Look
The Senate draft overall makes more changes to international tax policy than the House draft. On net the changes are positive.
8 min read
Senate Softens Blow for Pass-Throughs Using Current SALT Workarounds
The Senate’s version of the OBBB restores the benefit of avoiding the SALT deduction cap with PTETs for all pass-through businesses, while placing new limits on the extent of the workarounds.
6 min read
Breaking Down the Senior Deduction in the One, Big, Beautiful Bill
The House-passed reconciliation bill leaves out Trump’s promise to eliminate taxes on Social Security benefits, opting instead to expand the standard deduction for seniors.

“One Big Beautiful Bill Act” House GOP Tax Plan: Details and Analysis
Our preliminary analysis finds the tax provisions increase long-run GDP by 0.8 percent and reduce federal tax revenue by $4.0 trillion from 2025 through 2034 on a conventional basis before added interest costs.
9 min read
Trump Tariffs: Tracking the Economic Impact of the Trump Trade War
The tariffs amount to an average tax increase of nearly $1,200 per US household in 2025.
39 min read
A More Generous SALT Deduction Cap in the Big, Beautiful Bill Would Cost Revenue and Primarily Benefit High Earners
Letting the SALT cap slip further upwards would undercut the TCJA’s long-term legacy, worsening the fiscal outlook of the tax package and providing an unneeded benefit to higher earners.
4 min read
Current Trump Tariffs Threaten to Offset Benefits of Promised Tax Cuts
While Congress works on the “One, Big, Beautiful Bill” to cut taxes, President Trump has imposed significantly higher taxes by placing tariffs on more than 70 percent of US imports.
2 min read
The One Big Beautiful Bill, Explained
We break down the House GOP’s One, Big, Beautiful Bill—a sweeping tax package designed to extend key parts of the 2017 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act before they expire in 2026.

Three Corporate Tax Hikes That Would Undermine TCJA’s Improvements to Competitiveness
As lawmakers consider options for budgetary offsets, they should prioritize competitiveness and economic growth, as a heavier corporate tax burden will undermine the core purpose and achievement of the TCJA.
24 min read
House Tax Package Could Double Economic Growth Impact by Prioritizing Permanence for TCJA Business Provisions
As the current tax package stands, the House’s use of temporary policy is leaving most of the economic growth opportunities on the table.
2 min read
House “One Big Beautiful Bill” Riddled with Temporary Tax Policy
As lawmakers continue to debate the “One Big Beautiful Bill,” they should abandon temporary and complex policy in favor of simplicity and stability.
4 min read
House GOP’s Approach to the IRA Clean Energy Tax Credits: Five Things to Know
Tax simplification has two aspects. The first is a code without a mess of targeted provisions for various social policy goals. The second is a code with provisions that are simple and easy to comply with. The bill succeeds at the first, but fails at the second.
7 min read
Growth Should Be a Key Consideration if Corporate SALT Is Limited
Lawmakers should prioritize pro-growth tax policies and use the least economically damaging offsets to make the legislation fiscally responsible. If lawmakers choose to use C-SALT, they should carefully consider the economic trade-off with permanent, pro-growth tax cuts that support investment and innovation in the US.
7 min read
Overview of the Tax Foundation’s General Equilibrium Model
The Tax Foundation uses and maintains a General Equilibrium Model, known as our Taxes and Growth (TAG) Model to simulate the effects of government tax and spending policies on the economy and on government revenues and budgets.
9 min read
Making the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Permanent: Economic, Revenue, and Distributional Effects
Permanently extending the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act would boost long-run economic output by 1.1 percent, the capital stock by 0.7 percent, wages by 0.5 percent, and hours worked by 847,000 full-time equivalent jobs.
6 min read
New Directions in Tax Policy: Budgetary and Other Challenges of an Increasingly Complex Tax Code
The Tax Foundation, University of North Carolina Tax Center, and Massachusetts Institute of Technology Sloan School of Management are hosting a joint conference to discuss New Directions in Tax Policy: Budgetary and Other Challenges of an Increasingly Complex Tax Code.

Options for Navigating the 2025 Tax Cuts and Jobs Act Expirations
Policymakers should have two priorities in the upcoming economic policy debates: a larger economy and fiscal responsibility. Principled, pro-growth tax policy can help accomplish both.
21 min read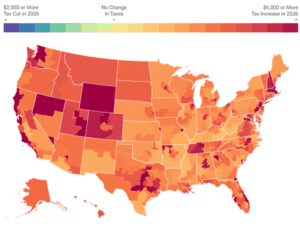
Expiring TCJA Tax Provisions in 2026 Would Produce Substantial Tax Hike across the US
At the end of 2025, the individual tax provisions in the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) expire all at once. Without congressional action, most taxpayers will see a notable tax increase relative to current policy in 2026.
4 min read
Tax Calculator: How the TCJA’s Expiration Will Affect You
Unless Congress acts, Americans are in for a tax hike in 2026.
3 min read
A Tax Reform Plan for Growth and Opportunity: Details & Analysis
This tax reform plan would boost long-run GDP by 2.5%, grow wages by 1.4%, and add 1.3M jobs, all while collecting a similar amount of tax revenue as the current code and reducing the long-run debt burden.
38 min readDownload a printable, one-page overview of the One, Big, Beautiful Bill, below.
Featured Experts
Have a question about any of the tax plans or policies above? Contact us to connect with a federal tax policy expert or click on the experts below to request them as a speaker at your upcoming event.
-
Erica York is Vice President of Federal Tax Policy with Tax Foundation’s Center for Federal Tax Policy. Her analysis has been featured in The Wall Street Journal, The Washington Post, Politico, and other national and international media outlets.
-
Alex Muresianu is a Senior Policy Analyst at the Tax Foundation, focused on federal tax policy. Previously working on the federal team as an intern in the summer of 2018 and as a research assistant in summer 2020. He attended Tufts University, graduating with a degree in economics and minors in finance and political science.



